New HA technologies make implementing redundancy strategies for PLCs/PACs and edge controllers easy and more economical
By Darrell Halterman - director for PACSystems controls products at Emerson?s machine automation solutions business
Increasing profitability, maximising plant uptime, and improving operational efficiency are all fundamental aims for manufacturers. Organisations are now seeking ways to reduce the causes of downtime that was once considered acceptable ? such as the need to replace a part on a failed device. To help them achieve these goals, they are increasingly looking to implement high availability (HA) technology and systems that help to ensure continuous operation. Industrial automation controllers, which can control a range of mission critical devices and applications, provide a key opportunity.
Distributed control systems have had in-built HA functions for a long time because large process plants, such as oil refineries, depend on them for continuous operation. In applications controlled by Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and programmable automation controllers (PAC), say for for machines and other equipment however, have typically only utilised HA functionality for the most critical applications. There are various reasons for this. First and foremost, typical failure rates of PLC, PAC and edge controllers have been acceptable for traditional operational availability requirements. Also, the processes for building and maintaining redundant PLC or edge controller architectures have frequently been complex and costly. As a result, simple spare part back-up often has been the most cost effective approach to mitigating a controller failure.
Now PLC, PAC and edge controllers, however, are playing increasingly critical roles in industrial applications, including key functions in data analysis and communications. At one time, a controller failure might have just taken a single machine offline, but today it can significantly impact uptime and efficiency of an entire plant or operation. For example, as newer lights-out manufacturing processes become more common in industries like electronics manufacturing and logistics or warehousing, the need for always-on control solutions are driving a new demand for HA controls architectures.
Adding a second controller
Modern PLC and controller technology makes it possible to implement HA in these systems easily, rapidly and at a cost not much greater than the traditional spare part model. This new HA approach to implementing controller redundancy increases uptime, mitigates risk and also supports stronger cybersecurity.
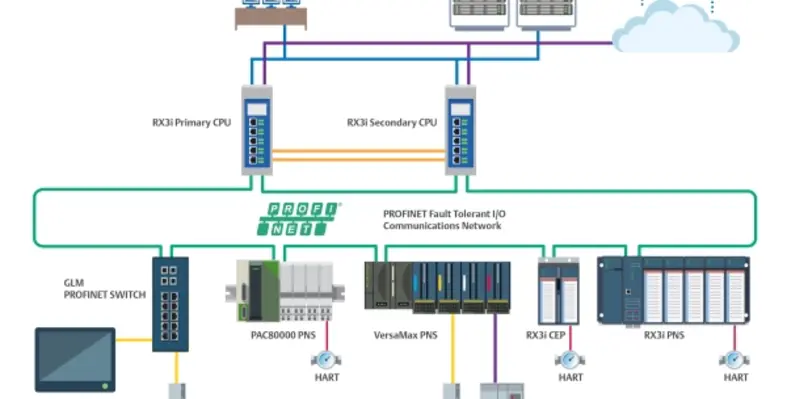
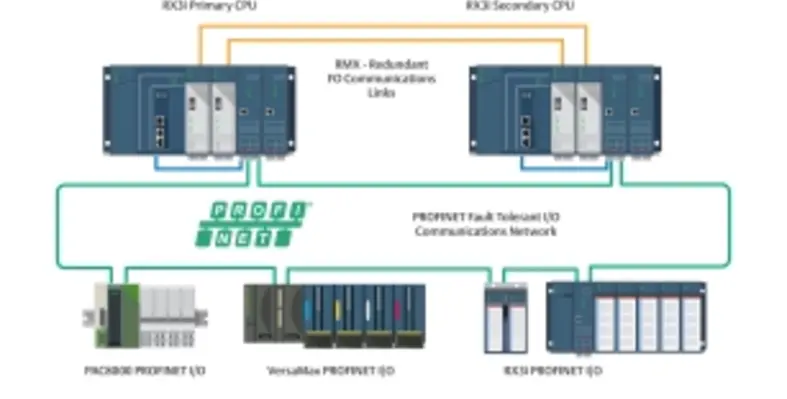
In modern PLC, PAC and edge controllers, such as the Emerson PACSystems RX3i controller, two paired controllers oversee systems by running in parallel, fully synchronised and lock-step execution in real time with access to the same I/O. The controller thus ceases to be a single point of failure, since a fault in the primary controller results in a bumpless transfer to the secondary controller in a matter of milliseconds. This is accomplished through reflective memory technology, which completely transfers an image of the necessary memory from an active controller to its pairedback-up controller with each individual scan.
Best-in-class HA control solutions implement a range of capabilities and conditions to provide consistent, deterministic reliable application control in cost effective and maintainable solutions. First, both controllers need the same access to all I/O and field devices, which is best achieved via a fault-tolerant Ethernet ring network. Creating an I/O ring network can often be achieved with minimal additional materials and effort when compared to traditional dual line or star networks.
Second, the two controllers need to communicate with each other over dedicated links designed to support lock-step synchronisation, scan for scan, so the back-up controller always has the same dataset as the active controller. These high-performance synchronisation links permit control failovers in a single PLC scan, which can be as fast as three milliseconds, depending on the configuration.The main benefit of the dedicated synchronisation links, however, is that the failover time is deterministic and not variable due to side-effects of other network devices or events. Other architectures that try to synchronise the two controllers via the I/O networks can result in control switchover lag due to interactions with other networked devices. In worst-case scenarios, the non-deterministic failover of these other architectures can cascade into additional system failures or even a total halt of both redundant controllers.
Third, while the two controllers can be installed in the same location, it is best to separate them geographically to avoid both being subject to common localised problems, such as power outages, fire or flood. The latest HA solutions use dedicated controller-to-controller links and supporting I/O networks, and can span distances of up to 10 km through the use of fibre optics.
Fourth, unlike some HA redundancy solutions that require two controllers to be the same hardware model and have identical software and firmware loads, the latest HA solutions are designed to continue seamless operations even with different software or firmware versions installed on the paired controllers. If the control software or firmware must be updated to deploy a new cybersecurity patch, the primary can be updated while the secondary runs and vice versa.Therefore, the machine or process does not need to be shut down as this critical cybersecurity work is performed.
The ability to update the control firmware, software, and even hardware while the application continues execution can help achieve additional economic benefits. Users may be able to perform routine maintenance and even upgrade activities while the application continues to operate. Activities that were once relegated to night and weekend shifts, meaning costly overtime, can now be performed during daylight shifts, without sacrificing production.
Summary
Organisations no longer have to sacrifice performance or solution cost in order to gain the many benefits of HA controls architectures. Modern control system redundancy architectures provide cost-effective HA solutions with fast, deterministic and consistent failovers. Application developers can now maximise their operational availability while minimising their maintenance costs, thus realising higher returns on their investments. Add to these the benefit of improved cybersecurity resiliency and HA controls architectures become a critical evolution in modern standard controls strategy.
For more information please visit here