As the UAE accelerates its national sustainability agenda, climate action is shifting from voluntary pledges to formal regulatory expectation. Federal Decree-Law No. 11 of 2024 on the Reduction of the Effects of Climate Change marks a turning point, introducing enforceable obligations around emissions management, alongside administrative penalties for non-compliance.
While the finer details of implementation and reporting pathways are still evolving, the direction of travel is clear.
Organisations are now expected to show real progress in measuring, managing, and governing their climate impact.
For many businesses, this represents more than a compliance update. It is a signal that sustainability data is moving into the same category as financial data, something boards and executives must understand, trust, and use to make decisions.
Against this backdrop, companies across sectors, from industry and real estate to logistics, finance, and investment, are reassessing how ESG data is generated and validated. We spoke with Jomy Joseph, Director at CoralDune Partners and former Regional Director for UL Solutions in the Middle East and Africa, about what Decree 11 means in practice and how organisations can respond without turning sustainability into a box-ticking exercise.
According to Joseph, adoption of the new law is already under way, but not in a uniform manner. “What I see on the ground is a phased adoption, rather than a single switch being flipped,” he says. Large groups, particularly those with international investors, lenders, or global customers, are leading the way. Many have been reporting emissions in some form for years, and Decree 11 is pushing them to tighten governance, improve data quality, and clarify accountability.
Assessing supply chains
The next wave, he explains, will come through supply chains. Contractors, manufacturers, logistics providers, and service companies are increasingly being asked to provide credible emissions data by customers who are themselves responding to regulatory and investor pressure.
For the mid-market, awareness is still uneven, but Joseph expects that to change quickly. “The UAE has made it clear through its Net Zero 2050 commitment and wider sustainability agenda that climate action is no longer optional. Decree 11 turns that ambition into a structured expectation.”
While the law allows for significant financial penalties, ranging from AED 50,000 up to AED 2,000,000 and rising for repeated violations, Joseph believes the earliest impacts will often be commercial rather than regulatory.
Companies may find themselves excluded from tenders where sustainability disclosure is part of the qualification process, subject to greater scrutiny from banks and insurers, or exposed to reputational risk if their figures cannot be supported with evidence. “Even before enforcement is felt directly, the market itself is already moving in the same direction as the regulation,” he notes.
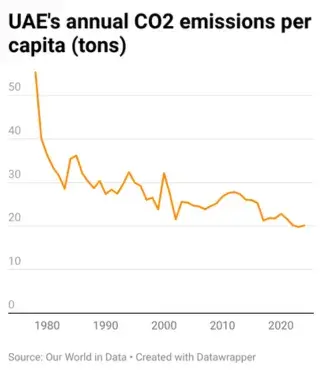
The UAE has supported initiatives to reduce emissions over the decades
At CoralDune Partners, Joseph and his team focus on helping boards and CEOs embed ESG reporting as a core governance and performance management function. Drawing on his background in testing, inspection, certification, and enterprise sustainability, he stresses that effective ESG reporting is not a marketing exercise. Instead, it starts with clarity around what actually matters for a specific business, sector, and geography.
That means defining a measurable baseline, agreeing on calculation methods, and ensuring consistency year on year. It also requires clear ownership, internal controls, and audit trails, so that reporting is defensible and repeatable.
Crucially, it involves building a practical roadmap that links emissions reduction to real operational levers, such as energy use, procurement, logistics, product design, and buildings. For mid-sized companies, the challenge is doing this without unnecessary complexity. “The goal is not to copy large enterprise reporting, but to build a credible, scalable foundation that leadership can rely on,” Joseph says.
Technology, and particularly AI, has a growing role to play. While spreadsheets remain familiar tools, Joseph argues they were never designed to support long-term, regulated reporting under investor scrutiny. AI can help automate data capture from invoices, fuel logs, utility bills, and ERP systems, classify it correctly, and flag anomalies before numbers reach management.
It also enables faster scenario planning, allowing companies to see how changes in suppliers, equipment, or logistics routes affect both emissions and cost. “The real issue is not the tool, but the outcome,” he says. “Can the organisation produce numbers that are consistent year after year, backed by evidence, and ready to be checked?”
Importantly, Decree 11 does not only apply to large enterprises. The focus is on activities and emissions sources, not company size. Smaller businesses and startups should not assume they are automatically out of scope.
For them, compliance does not mean producing lengthy reports. A basic emissions baseline, clear calculation records, and a short list of practical actions that reduce both cost and emissions are often enough to start. Many will first feel the impact through customer and supply chain requirements. Being prepared early puts them in a far stronger position.
Challenges ahead
One of the biggest issues Joseph sees is trust in the data itself. Many organisations can produce a sustainability statement, but far fewer can clearly explain where the numbers came from and whether the same approach will be used next year. This is where ESG reporting becomes a board-level issue, as weak data translates directly into regulatory, commercial, and reputational risk.
To reduce greenwashing risk, Joseph points to the importance of moving from claims to evidence and assurance. Structured measurement, reporting, and verification processes, independent assurance under standards such as ISO 14064-3, product-level tools like life cycle assessments and environmental product declarations, and recognised built environment frameworks all help convert intent into measurable performance. “If a claim cannot be supported with data and documentation, it should not be made,” he says.
Globally, Joseph sees useful benchmarks in the European Union’s focus on structure and comparability, Singapore’s practical and business-friendly approach, and the UK’s emphasis on transition planning. The UAE, he believes, has the advantage of speed. With strong digital government infrastructure and clear national targets, it has the potential to move rapidly from policy to execution.
Ultimately, credible ESG reporting is becoming inseparable from competitiveness. As sustainability data increasingly shapes access to capital, insurance, and investment, Decree 11 is not just about compliance. It is about how companies position themselves for the next phase of growth in a low-carbon economy.